

#Function of free nerve endings in skin skin#
Mechanoreceptors are present in the superficial as well as the deeper layer of skin and near bone. Daley of North Carolina Wesleyan College. The external stimuli are usually in the form of touch, pressure, stretching, sound waves, and motion. CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list ( link) Stretch-sensitive muscular-free nerve endings". Their role is to transduce peripheral stimuli they include. They are slow to adjust to a stimulus and so are less sensitive to abrupt changes in stimulation. Free nerve endings are sensitive to painful stimuli, to hot and cold, and to light touch. "Neural mechanisms underlying the clasp-knife reflex in the cat. The dermis contains the majority of free afferent nerve endings originating in the skin. Free nerve endings are the most common nerve endings in skin, and they extend into the middle of the epidermis. Textbook in Medical Physiology And Pathophysiology: Essentials and clinical problems.A person is administered a placebo 'pain-relieving' skin cream just before receiving a painful electric shock. "Free nerve ending terminal morphology is fiber type specific for A delta and C fibers innervating rabbit corneal epithelium". Meissners Corpuscles consist of an ovoid structure within which the nerve ending branches and orients parallel to the surface of the skin. The most effective site for the induction of analgesia in rats using electrical stimulation is the Periaqueductal gray matter. Aδ fibres are fast-adapting, while C fibers are slow-adapting. The majority of Aδ (A delta) fibers (group III) and C (group IV) fibers end as free nerve endings.ĭifferent types of FNE can be fast-adapting, intermediate, or slow-adapting. Some FNEs can also detect stretch stimuli. The anatomy of the fine, varicose free nerve endings of the Rohon-Beard cell neurites is discussed in relation to their function in detecting transient.
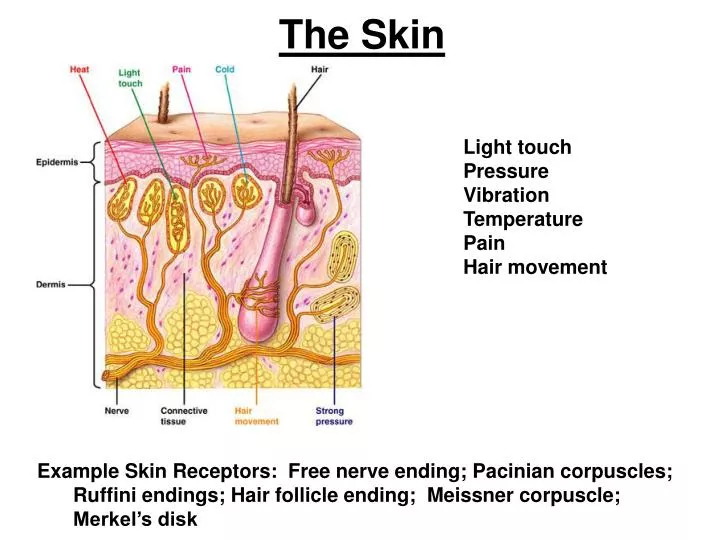
These nerve endings are responsible for detecting temperature, mechanical stimuli (such as pressure), pain (nociception), and information about touch. They penetrate the epidermis and end in the stratum granulosum. However, the term of free nerve-ending has to be considered prudently since nerve endings are always in close apposition with keratinocyte or Langherans cell. They are the most common type of nerve ending, and are most frequently found in the skin. Free nerve endings are unencapsulated and have no complex sensory structures, unlike those found in Meissner's or Pacinian corpuscles. English: Tactile corpuscule Latin: Corpusculum tactus Synonim: Meissner's corpuscle. A free nerve ending ( FNE) is an unspecialized, afferent nerve ending, meaning it brings information from the body's periphery to the brain. The tactile corpuscles are most densely concentrated in the portions of the skin that are sensitive to light touch, especially in the skin of palms, fingers and lips.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
